One should be mixed with alkaline fertilizer or applied at the same time. Alkaline fertilizers include plant ash, lime, calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer, steel slag phosphate fertilizer, and the like. If mixed urea is applied or applied at the same time, the nitrogen in the urea will be aggravated by ammonia. Therefore, in summer and autumn, urea and alkaline fertilizer should be staggered for 3 to 4 days, and winter and spring should be staggered for 7 to 8 days.
Two bogey for seed fertilizer. Urea is used as a seed fertilizer. Due to the toxic effects of concentrated biuret, the seeds lose their germination power and endanger the seedlings. At the same time, because high concentration of urea can destroy the protein structure of the seed, it is also toxic and inhibiting to the seed, so it is not suitable for seed fertilizer. If it is necessary to apply as a seed fertilizer, avoid contact with seeds and fertilizers and control the dosage.
Watering immediately after the three bogey. The amide nitrogen has a low adsorption capacity with the soil colloid, and its fluidity and leaching in the soil is not smaller than that of the nitrate nitrogen. In view of these properties of urea, after surging urea, do not water before it is not converted, otherwise the waste is large. Generally, summer and autumn seasons should be watered 2 to 3 days after application, and winter and spring seasons should be watered after 7 to 8 days. Rice should be controlled by urea in the shallow water layer. After the application, the cultivating should be carried out to make the soil and fertilizer melt. Before the heavy rain, urea could not be applied.
Four bogey shallow application. Urea shallow nutrient is volatile and easy to be consumed by weeds. Deep application of urea, melt fertilizer in the soil, so that the fertilizer is in the moist soil layer, is conducive to the performance of fertilizer. For the topdressing should be applied to the seedlings or the ditch on the side of the seedling, the depth should also be about 10 to 15 cm. In this way, urea can be concentrated in the root dense layer by moving, which is convenient for crop absorption and utilization.
Five bogey usage is too large. The nitrogen content of urea is 44% to 48%, the nutrient content is high, and the application amount should not be too large, so as to avoid unnecessary waste and “fat damageâ€. Generally, the application amount per acre of dry land is 5 to 15 kg, and the application amount per acre of paddy field is 15 Up to 20 kg.
Six bogey high concentration foliar application. Foliar spray should avoid excessive concentration of urea solution, otherwise it will burn out the leaves and poison the plants. Generally, the concentration of corn, wheat, rice, and cotton is preferably 2%; vegetables and fruits are preferably 0.5% to 1%; and fruit trees are preferably 0.5% to 1.5%.
Seven bogey is applied too late. The application of urea too late is not conducive to the exertion of fertilizer efficiency, and it is easy to cause crops to be late and ripe, so it should be applied 4 to 7 days earlier than other nitrogen fertilizers.
Eight bogey single application. Urea should be combined with organic fertilizers and phosphorus and potassium fertilizers to meet the needs of various nutrients in crops. For example, when urea is mixed with superphosphate, the unstable ammonium hydrogen sulfate can be converted into stable ammonium phosphate, which can accelerate the conversion and decomposition of urea, so that the available nitrogen can be quickly absorbed by the crop and improve the utilization rate of urea.
Source: Tianjin Daily Author: Xue Yanli
Optical filters are devices that selectively transmit light of different wavelengths
optical filters include an extensive collection of dielectric-coated filters, colored glass filters, neutral density filters, spatial filters, and a tunable optical filter based on liquid crystal technology.
Color glass filter, Neutural density, IR cut, Narrow Bandpass Filter,notch filter Birefringent filter, IPL filter, biochemical analyzer filter.
Filters are ideal for a variety of applications, such as fluorescence microscopy, spectroscopy, clinical chemistry, or imaging. These filters are typically used in the life science, industrial, or R&D industries
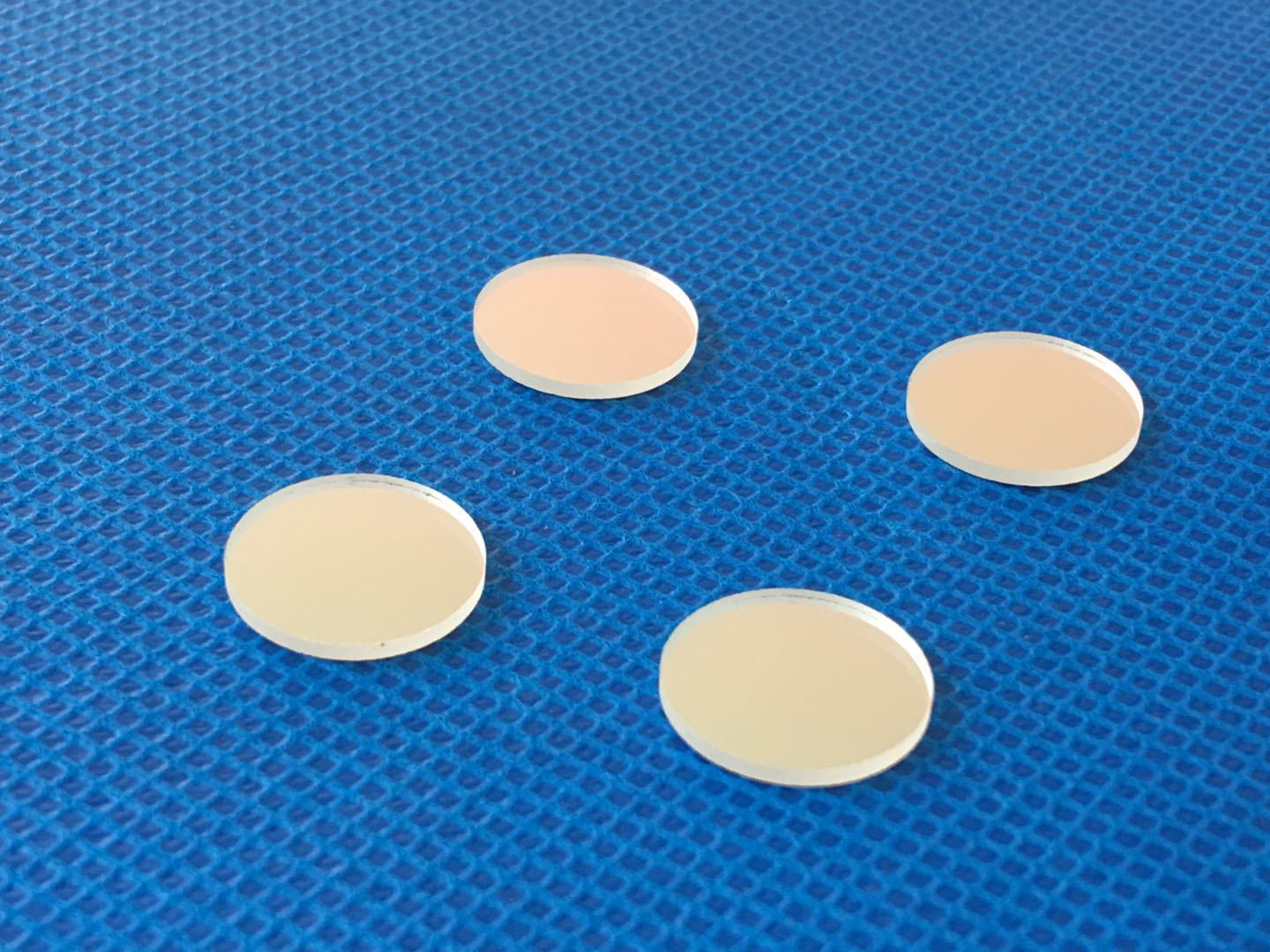
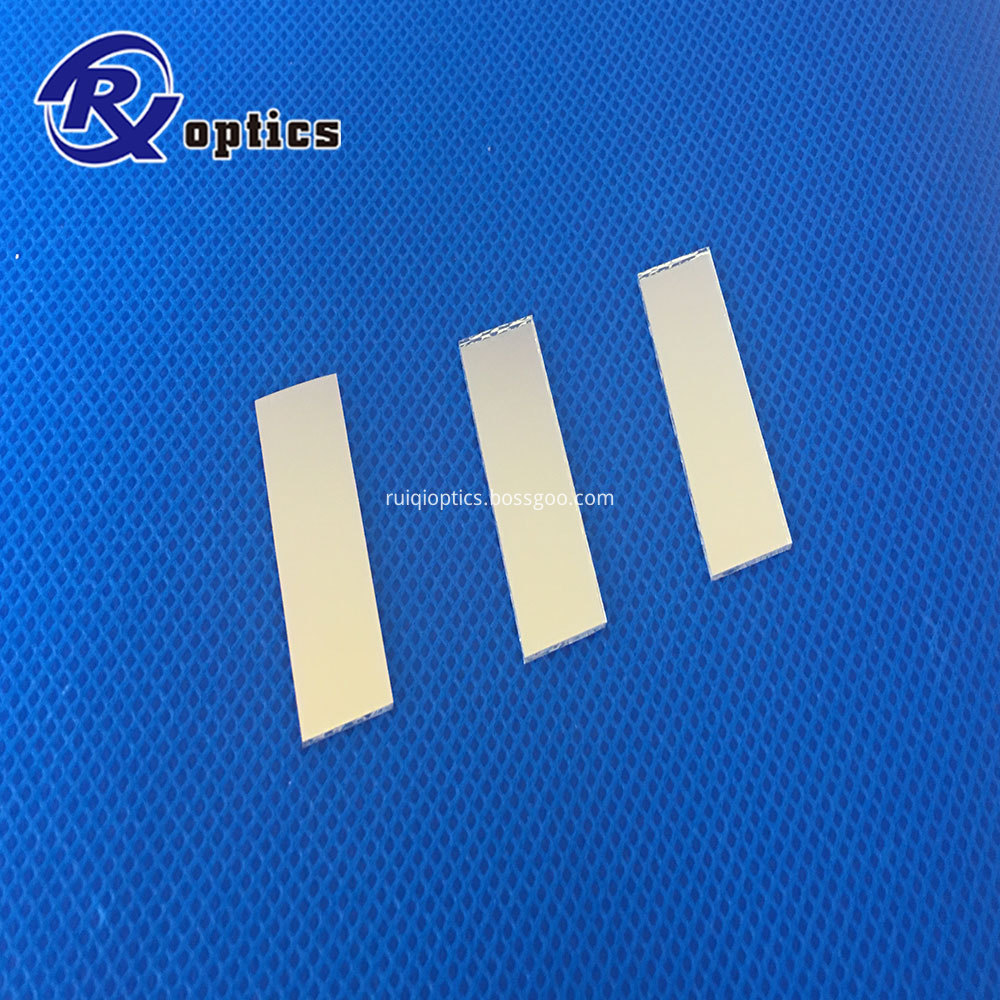
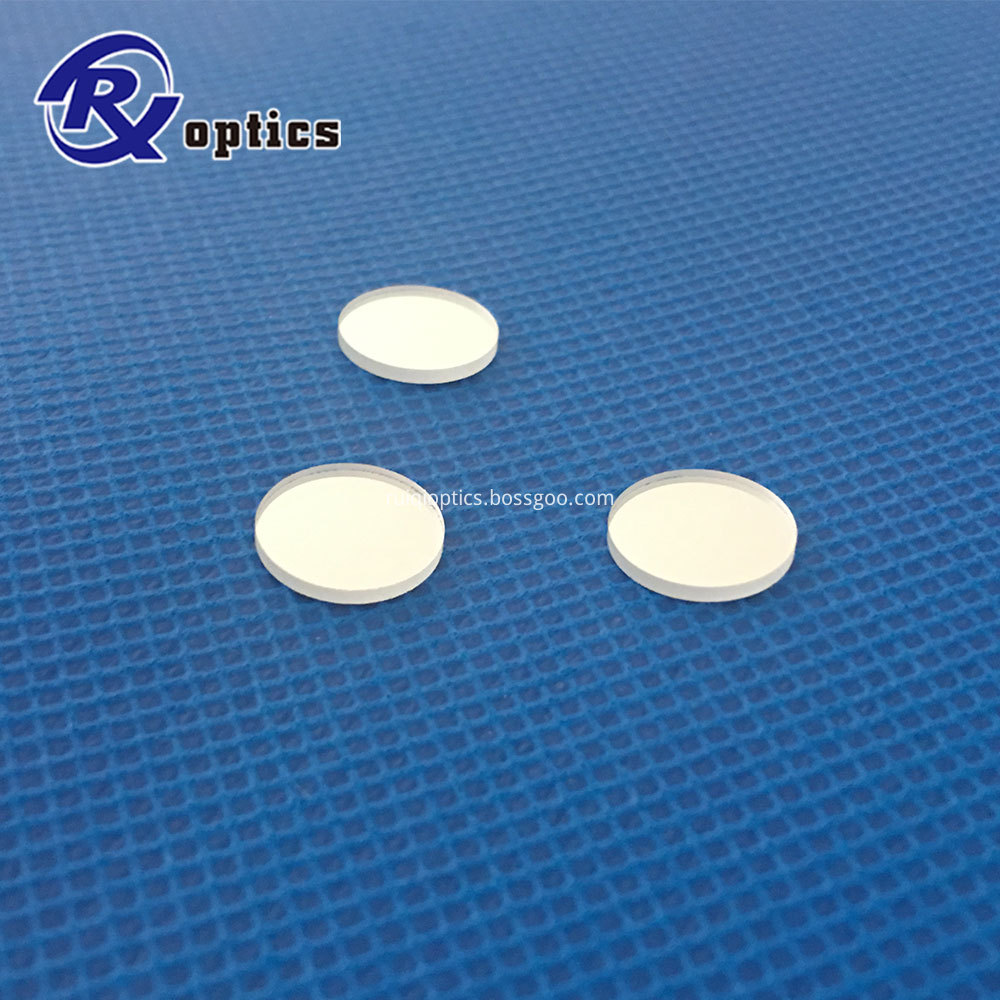
Optical Filters,Glass Optical Filters,Optical Plastic Filter,Narrow Bandpass Optical Filter
Changchun Ruiqi Optoelectronics Co.,Ltd , https://www.ruiqi-optics.com