Two-dimensional nanomaterials of transition metal sulfides are another important class of two-dimensional semiconductor nanomaterials after graphene. In particular, its tunable bandgap characteristics in the near-infrared region have unique advantages in the development of new optoelectronic functional devices. Recently, the researcher of the Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wang Jun, Research Group made a number of advances in the preparation, characterization and nonlinear optical properties of two-dimensional semiconductor materials.
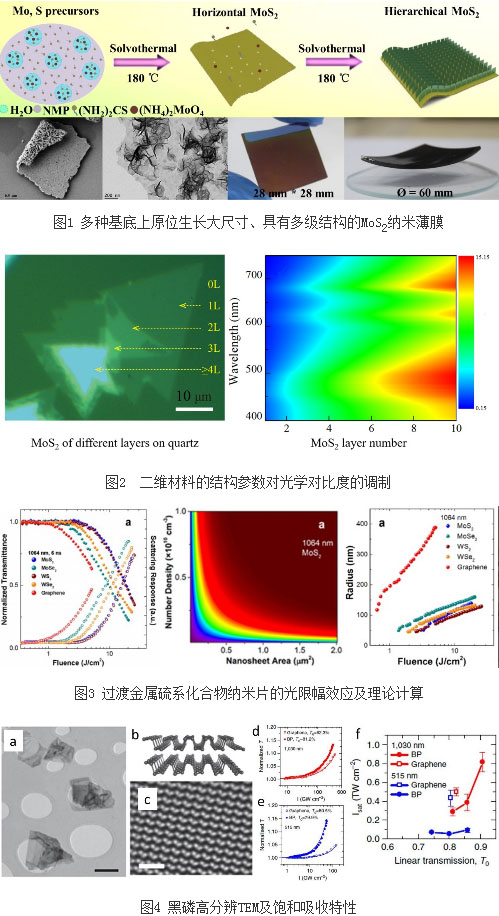
One of the bottlenecks in transition metal sulfide nanomaterials during the deviceization process is the synthesis of low-cost, large-size two-dimensional materials. The research team (Zhang Xiaoyan et al.) designed and synthesized special morphologies using in situ growth solvothermal techniques. MoS2 nano films. The solvothermal method, which breaks through traditional hydrothermal synthesis techniques, can only achieve the limitations of micron-sized nanosheets. It uses the “organic solvent-water†system to grow in situ on various substrates such as quartz, silicon wafers, optical fibers, and curved surfaces. Continuous, large-size, controllable MoS2 film. Studies have shown that the third-order nonlinear absorption coefficient of this multi-layered MoS2 thin film in the near-infrared region is much higher than the third-order nonlinear absorption coefficient of the MoS2 thin film obtained by the vacuum filtration re-group deposition technique, which is due to its Unique hierarchical structure. Related papers have been published online by Nanoscale magazine [Nanoscale, 8, 431, (2016)].
The structural microscopic analysis of two-dimensional nanomaterials is of great significance for the study of the physical properties and deviceization of such materials. Based on this, the research group (Li Yuanxin) and others proposed using the optical transmission characteristic matrix to simulate the optical contrast of a two-dimensional layered nanomaterial and studied its dependence on the substrate and the incident light wavelength. This method was used to calculate the contrast of MoS2 layers prepared by chemical vapor deposition under white light irradiation. Theoretical simulations are in good agreement with experimental results. Compared with the traditional Fresnel theory, this method is faster, simpler, and more accurate, and can effectively guide the choice of two-dimensional nanomaterial substrates and irradiation sources. Related papers have been published online by Nanoscale Magazine (DOI: 10.1039/C5NR06287J).
The research group (Dong Ningning et al.) also systematically studied the visible-near-infrared broadband optical limiting effect of liquid-suspended transition metal sulfide 2D nanomaterials under nanosecond pulsed laser irradiation. Studies have shown that selenide in the near-infrared region has more excellent optical limiting characteristics than sulfides. Based on the liquid dispersion system, the innovation proposes a method for calculating the number density of nanosheets, and establishes the relationship between the laser energy and the scattering center size, which is very important for studying the optical limiting effect induced by Mie scattering in transition metal chalcogenide compounds. Related papers are published in Scientific Reports (5, 14646).
The research group (Zhang Saifeng, etc.) and Trinity University in Dublin, Ireland, have verified the broadband ultra-fast nonlinear optical effect of the new two-dimensional material, black phosphorus, and confirmed that it has more excellent saturation absorption than graphene, and predicted layered black. Phosphorus has potential for application in the development of mode-locked and Q-switched devices. The paper was published in Nature communications [Nature communications, 6, 8563, (2015)] and was highly evaluated and cited by research groups such as Nanyang Technological University, Wroclaw University of Technology, and Phys.org and MIT Technology Review. It is the first report of the saturation absorption effect of black phosphorus.
In addition, the topical panel published in 2015 Photonics Research inviting paper Tunable a minimum refractive index of two-dimensional MoS2, WS2, and MoSe2 nanosheet dispersions were selected "Photonics Research magazine downloads in 2015 the top ten papers."
Cold storage room fast door are used to industrial warehouse applications, our cold storage doors combine the latest technology, premium materials and design features to meet the demanding requirements of the cold storage industry. Available as a sliding, swing and vertical lift door, all Cold Guard doors incorporate a tough and thermally neutral fiberglass reinforced pultrusion framework, extruded plastic polymer casings and Non-CFC foamed-in place polyurethane core. We understand the conditions that cold storage doors must endure. Superior design methods and non-corrosive materials ensure that Cold Guard will perform and look good for years to come!
The advantages of cold storage fast room door
Excellent Insulation Properties
Save Money on Temperature Costs
A Variety of Cold Room Options
Temperature Control and Efficiency
One of the most important benefits of our cool room panels is passive temperature control.
Safety for You Too
Not only are our cold room panels very hygienic, they also allow for superior safety. Their low allergenic qualities and enhanced seismic performance will protect you while you`re at work.
Cold Storage Room Fast Door,Freezer Room Fast Door,Freezer Room Insulated Fast Door,Thick Curtain High Speed Door
Shenzhen Hongfa Automatic Door Co., Ltd. , https://www.hongfadoor.com