Abstract: Superhard tools are widely used in metal cutting, wood processing, mining and petroleum exploration. However, due to its high hardness and good wear resistance, it is difficult to form it by conventional methods. The paper discusses the principle of super-hard tool EDM and its pulse power supply, and conducts an experimental study on the influence of electrical parameters on sharpening efficiency and surface roughness.
Superhard tools mainly refer to polycrystalline diamond and polycrystalline cubic boron nitride tools. This type of tool is widely used in metal cutting, wood processing, mining and petroleum exploration due to its high hardness, good wear resistance and ideal processing quality. However, its processing and forming is difficult, and the development of its processing technology is still a research topic in the world today. At present, the processing methods of superhard tools mainly include mechanical grinding, ultrasonic machining and electric spark grinding. Mechanical grinding is the most commonly used processing method, but it requires expensive diamond grinding wheel and high-rigidity grinding machine, which has low processing efficiency and large grinding wheel loss. Ultrasonic machining is mainly used for polishing superhard tools, and its coarse and medium polishing efficiency is low. The consumption of diamond abrasive powder is large; EDM grinding is an effective processing method with low cost and high processing precision. The author has been engaged in the research of super-hard material EDM process for many years. In view of the shortcomings of low power productivity and low energy utilization rate of pulse power supply, combined with the characteristics of super-hard tool EDM, the transistor-switched high-voltage PLC pulse has been developed. power supply. And the experimental research on its processing technology.
Superhard tool EDM is also an EDM. Similar to ordinary EDM, super-hard tool EDM is also based on the electrical corrosion phenomenon of pulsating spark discharge between the tool and the workpiece in the insulating medium to remove excess metal to achieve the size, shape and surface of the part. Quality requirements; unlike ordinary EDM, EDM is a rotating disc electrode as a tool, and the machining current is often smaller; EDM is similar to conventional diamond grinding, due to electricity Spark grinding uses graphite or copper electrodes instead of relatively expensive diamond wheels, which are much less expensive to machine. The principle of super-hard tool EDM is shown in Figure 1.
The workpiece and oil sump are placed on a CNC table. The tool electrode is a copper disc. During processing, the DC motor drives the tool electrode to rotate at a high speed. At the same time, the workpiece performs a servo feed motion on the one hand in the Y-axis direction and a reciprocating motion on the X-axis direction on the other hand. This allows the disk electrode loss to be distributed over as large a surface as possible, so that its geometric accuracy can be stably maintained for a long time. Compared with ordinary EDM, the super-hard tool EDM has the following advantages due to the rotation of the electrode and the reciprocating motion of the table:
It is well known that superhard materials have high melting point, high electrical resistivity and good thermal conductivity in addition to superhard wear resistance. Such materials are not only difficult to machine, but also difficult to process. A large number of experiments have shown that EDM grinding of superhard materials by conventional pulse power supply is not easy to obtain satisfactory results. The ideal pulse power supply should have highly concentrated pulse discharge energy, strong discharge explosive force and high peak voltage ( Generally greater than 200V). As we all know, the RC pulse power supply that usually processes metal can get a very high spike current in a short time, so its instantaneous discharge explosive force is large; in addition, the RC pulse power supply is especially suitable for finishing, so that the normal RC pulse power supply is given. Applying a high voltage, that is, making a high-voltage RC pulse power supply, may achieve the purpose of effectively EDM grinding superhard materials. However, if the method of simply applying a high voltage to the RC pulse power supply is inevitably, there is a disadvantage that the RC pulse power source has low productivity and low power utilization. Based on the above analysis, the author combines the characteristics of super-hard tool EDM to design a transistor-switched high-voltage RC pulse power supply, which can improve the productivity and power utilization of super-hard tool EDM and can be obtained. Surface roughness values ​​and sharp edges. However, in actual processing, it is found that as the current limiting resistor is reduced, the transistor is easily broken down. To this end, an inductor is connected in series after the current limiting resistor R, and is designed as a transistor switching type high voltage PLC pulse power supply as shown in FIG. The working principle is as follows: after the DC power source E is turned on, the transistor T is turned on, and the power source charges the capacitor C through the current limiting resistor R, the inductor L and the transistor T. When the voltage across the capacitor rises to the inter-electrode gap breakdown voltage, the pole The dielectric is broken down to form a discharge channel, and the discharge current instantaneously forms a pulse voltage across the high-speed switching diode. This pulse voltage causes the optocoupler in the ultra-high speed optocoupler sampling circuit to be turned on quickly, and outputs a trigger pulse to trigger 555. The delay circuit causes the output signal of 555 to be inverted, and the transistor T is quickly turned off after being shaped by the shaping circuit, and the transistor T is turned on again after a period of time. The DC power source is charged to the capacitor C via R, L, and T. A series of processing pulses are formed in this manner. The delay length of the delay circuit can be adjusted according to the gap discharge condition. In this way, once the gap is generated, the transistor T is turned off, so that the DC power source E is completely separated from the discharge circuit, and the DC power source does not affect the gap discharge condition.
The current limiting resistor R in the power supply is a high-power wirewound resistor, which is connected in series with the inductor L. When the transistor is momentarily turned off, a high peak voltage is generated at the collector terminal, which easily breaks down the transistor. To this end, the freewheeling diode D 1 is connected, and R and L form a bleeder circuit. Since processing polycrystalline diamond and polycrystalline cubic boron nitride requires a supply voltage of up to several hundred volts. Therefore, the transistor T must use a high power transistor with a high withstand voltage. D 2 is a high-power damper diode that dampens the negative half-wave and reduces electrode losses. The sampling diode uses a fast switching diode, the optocoupler uses an ultra-high speed optocoupler 6N137, and the components in the delay circuit and the shaping circuit are required to have a high response speed, otherwise it is difficult to track the gap discharge condition.
There is also a problem that must be paid attention to in the design of the power supply, that is, the acquisition of a high voltage power supply. Because the power supply voltage required to process polycrystalline diamond and polycrystalline cubic boron nitride is as high as several hundred volts or even thousands of volts. It is highly undesirable that such a high voltage is directly obtained by the transformer. Because the high voltage AC power is very dangerous in the actual operation of the factory. The simplest solution is to use a voltage doubler rectifier circuit. However, one drawback of this circuit is that the output current is small, and the output current is smaller as the multiple of the voltage doubler rectifier circuit increases. Fortunately, the super-hard tool EDM sharpening area is not large, and the average machining current required is not very large. Therefore, it is still preferable to use a double voltage rectification circuit.
Productivity and surface roughness are the two main technical indicators of super-hard tool EDM. In order to obtain good surface roughness, the power parameters during coarse, medium and fine grinding must be selected. The following is an experimental study on the effects of electrical parameters on the EDM grinding efficiency and surface roughness of superhard tools. In the experiment, the electrode material is copper, the workpiece material is polycrystalline diamond, the working fluid is kerosene, and the positive electrode is processed.
Superhard tools mainly refer to polycrystalline diamond and polycrystalline cubic boron nitride tools. This type of tool is widely used in metal cutting, wood processing, mining and petroleum exploration due to its high hardness, good wear resistance and ideal processing quality. However, its processing and forming is difficult, and the development of its processing technology is still a research topic in the world today. At present, the processing methods of superhard tools mainly include mechanical grinding, ultrasonic machining and electric spark grinding. Mechanical grinding is the most commonly used processing method, but it requires expensive diamond grinding wheel and high-rigidity grinding machine, which has low processing efficiency and large grinding wheel loss. Ultrasonic machining is mainly used for polishing superhard tools, and its coarse and medium polishing efficiency is low. The consumption of diamond abrasive powder is large; EDM grinding is an effective processing method with low cost and high processing precision. The author has been engaged in the research of super-hard material EDM process for many years. In view of the shortcomings of low power productivity and low energy utilization rate of pulse power supply, combined with the characteristics of super-hard tool EDM, the transistor-switched high-voltage PLC pulse has been developed. power supply. And the experimental research on its processing technology.
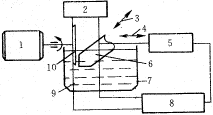 1. DC motor 2. Pulse power supply 3. Reciprocating motion 4. Servo motion 5. Servo control 6. Workpiece 7. Oil sump 8. Discharge gap detection 9. Kerosene 10. Disc electrode Figure 1 Schematic diagram of super-hard tool EDM |
1 Principle of super-hard tool EDM
Superhard tool EDM is also an EDM. Similar to ordinary EDM, super-hard tool EDM is also based on the electrical corrosion phenomenon of pulsating spark discharge between the tool and the workpiece in the insulating medium to remove excess metal to achieve the size, shape and surface of the part. Quality requirements; unlike ordinary EDM, EDM is a rotating disc electrode as a tool, and the machining current is often smaller; EDM is similar to conventional diamond grinding, due to electricity Spark grinding uses graphite or copper electrodes instead of relatively expensive diamond wheels, which are much less expensive to machine. The principle of super-hard tool EDM is shown in Figure 1.
The workpiece and oil sump are placed on a CNC table. The tool electrode is a copper disc. During processing, the DC motor drives the tool electrode to rotate at a high speed. At the same time, the workpiece performs a servo feed motion on the one hand in the Y-axis direction and a reciprocating motion on the X-axis direction on the other hand. This allows the disk electrode loss to be distributed over as large a surface as possible, so that its geometric accuracy can be stably maintained for a long time. Compared with ordinary EDM, the super-hard tool EDM has the following advantages due to the rotation of the electrode and the reciprocating motion of the table:
- The rotation of the electrode and the reciprocating motion of the table facilitate the discharge of the electro-erosion product and the dispersion and transfer of the discharge point, and it is not easy to cause the phenomenon of carbon arcing. This improves the stability of the process.
- The rotation of the electrode facilitates the rapid deionization of the discharge channel at the end of the pulse discharge, which improves the pulse utilization rate and thereby improves the productivity of the grinding process.
2 Principle and composition of transistor switching high voltage PLC pulse power supply
It is well known that superhard materials have high melting point, high electrical resistivity and good thermal conductivity in addition to superhard wear resistance. Such materials are not only difficult to machine, but also difficult to process. A large number of experiments have shown that EDM grinding of superhard materials by conventional pulse power supply is not easy to obtain satisfactory results. The ideal pulse power supply should have highly concentrated pulse discharge energy, strong discharge explosive force and high peak voltage ( Generally greater than 200V). As we all know, the RC pulse power supply that usually processes metal can get a very high spike current in a short time, so its instantaneous discharge explosive force is large; in addition, the RC pulse power supply is especially suitable for finishing, so that the normal RC pulse power supply is given. Applying a high voltage, that is, making a high-voltage RC pulse power supply, may achieve the purpose of effectively EDM grinding superhard materials. However, if the method of simply applying a high voltage to the RC pulse power supply is inevitably, there is a disadvantage that the RC pulse power source has low productivity and low power utilization. Based on the above analysis, the author combines the characteristics of super-hard tool EDM to design a transistor-switched high-voltage RC pulse power supply, which can improve the productivity and power utilization of super-hard tool EDM and can be obtained. Surface roughness values ​​and sharp edges. However, in actual processing, it is found that as the current limiting resistor is reduced, the transistor is easily broken down. To this end, an inductor is connected in series after the current limiting resistor R, and is designed as a transistor switching type high voltage PLC pulse power supply as shown in FIG. The working principle is as follows: after the DC power source E is turned on, the transistor T is turned on, and the power source charges the capacitor C through the current limiting resistor R, the inductor L and the transistor T. When the voltage across the capacitor rises to the inter-electrode gap breakdown voltage, the pole The dielectric is broken down to form a discharge channel, and the discharge current instantaneously forms a pulse voltage across the high-speed switching diode. This pulse voltage causes the optocoupler in the ultra-high speed optocoupler sampling circuit to be turned on quickly, and outputs a trigger pulse to trigger 555. The delay circuit causes the output signal of 555 to be inverted, and the transistor T is quickly turned off after being shaped by the shaping circuit, and the transistor T is turned on again after a period of time. The DC power source is charged to the capacitor C via R, L, and T. A series of processing pulses are formed in this manner. The delay length of the delay circuit can be adjusted according to the gap discharge condition. In this way, once the gap is generated, the transistor T is turned off, so that the DC power source E is completely separated from the discharge circuit, and the DC power source does not affect the gap discharge condition.
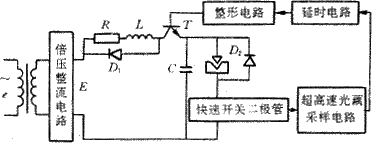 Figure 2 Schematic diagram of transistor switching high-voltage PLC pulse power supply |
The current limiting resistor R in the power supply is a high-power wirewound resistor, which is connected in series with the inductor L. When the transistor is momentarily turned off, a high peak voltage is generated at the collector terminal, which easily breaks down the transistor. To this end, the freewheeling diode D 1 is connected, and R and L form a bleeder circuit. Since processing polycrystalline diamond and polycrystalline cubic boron nitride requires a supply voltage of up to several hundred volts. Therefore, the transistor T must use a high power transistor with a high withstand voltage. D 2 is a high-power damper diode that dampens the negative half-wave and reduces electrode losses. The sampling diode uses a fast switching diode, the optocoupler uses an ultra-high speed optocoupler 6N137, and the components in the delay circuit and the shaping circuit are required to have a high response speed, otherwise it is difficult to track the gap discharge condition.
There is also a problem that must be paid attention to in the design of the power supply, that is, the acquisition of a high voltage power supply. Because the power supply voltage required to process polycrystalline diamond and polycrystalline cubic boron nitride is as high as several hundred volts or even thousands of volts. It is highly undesirable that such a high voltage is directly obtained by the transformer. Because the high voltage AC power is very dangerous in the actual operation of the factory. The simplest solution is to use a voltage doubler rectifier circuit. However, one drawback of this circuit is that the output current is small, and the output current is smaller as the multiple of the voltage doubler rectifier circuit increases. Fortunately, the super-hard tool EDM sharpening area is not large, and the average machining current required is not very large. Therefore, it is still preferable to use a double voltage rectification circuit.
3 Experimental results and analysis
Productivity and surface roughness are the two main technical indicators of super-hard tool EDM. In order to obtain good surface roughness, the power parameters during coarse, medium and fine grinding must be selected. The following is an experimental study on the effects of electrical parameters on the EDM grinding efficiency and surface roughness of superhard tools. In the experiment, the electrode material is copper, the workpiece material is polycrystalline diamond, the working fluid is kerosene, and the positive electrode is processed.
- The effect of resistance on processing productivity
- Effect of power supply voltage on processability
- The effect of capacitance on processability
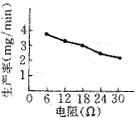 Figure 3 Relationship between resistance and productivity |
Figure 3 shows the effect of resistance on processing productivity. Experimental conditions: The capacitance is 1 μF, the inductance is 0.025H, and the voltage is 260V. As can be seen from the figure, the processing productivity decreases as the resistance value increases. The reason is that as the resistance value increases, the charging time of the capacitor is prolonged, resulting in a decrease in the pulse frequency. As can be seen from the formula (1), the processing productivity decreases as the pulse frequency decreases. Therefore, the productivity decreases as the resistance value increases. It can also be seen from the figure that the current limiting resistor can be made small by using a high power transistor as a switching element.
| MRR=K a W M fØ | (1) |
The influence of the power supply voltage on the processing performance is shown in Figures 4 and 5. Experimental conditions: capacitance is 1 μF, inductance is 0.025H, and resistance is 24 W. As can be seen from Figure 4, the productivity increases as the supply voltage increases. This is because when the power supply voltage rises, in order to stabilize the processing, the inter-electrode discharge gap must be increased accordingly. This also increases the breakdown voltage value between the poles accordingly. The breakdown voltage has the following relationship with a single pulse energy.
| W m =0.5CU j 2 | (2) |
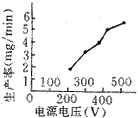 Figure 4 Relationship between power supply voltage and productivity | 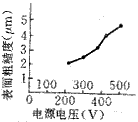 Figure 5 Relationship between surface roughness of power supply voltage |
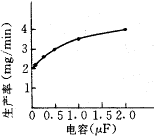 Figure 6 Relationship between capacitance and productivity | 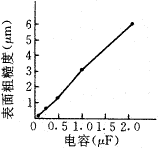 Figure 7 Relationship between capacitance and surface roughness |
Figure 5 is a plot of supply voltage versus surface roughness. As can be seen from the figure, the surface roughness value increases as the power supply voltage increases. It can be seen from the previous analysis that as the power supply voltage increases, the single pulse discharge energy increases, and the increase of the single pulse discharge energy will result in an increase in the surface roughness value. Therefore, as the power supply voltage increases, the surface roughness value increases.
Figures 6 and 7 show the effect of the capacitance on the processing performance. Experimental conditions: resistance is 24 W , inductance is 0.025H, and voltage is 260V. As can be seen from Fig. 6, the productivity increases as the capacitance increases, and tends to be saturated. This is similar to a normal RC pulse power supply. It can be seen from Fig. 7 that the surface roughness value increases as the capacitance increases. It can be seen from equation (2) that a single pulse energy increases with an increase in capacitance, and an increase in a single pulse energy results in an increase in surface roughness value. Therefore, the surface roughness value increases as the capacitance increases.
4 Conclusion
- Since a high-power transistor is used as the switching element, the transistor is quickly turned off once the breakdown discharge is generated, so that the DC power source is isolated from the discharge gap, the discharge loop is not affected by the DC power supply, and the processing process is stable; and the current limiting resistor can be made small. Increased pulse frequency. This enables ultra-hard tool EDM grinding with high efficiency, low energy consumption and low electrode loss.
- When an electric spark finishes an ultra-hard tool, arc discharge is likely to occur due to a small capacitance. By using a transistor as a switching element, the pulse stop time can be adjusted by adjusting the length of the delay, so that the discharge channel is completely deionized. Thereby a small surface roughness value is obtained.
- It can be seen from the experiment that the super-hard tool EDM sharpening productivity decreases with the increase of the resistance value, increases with the increase of the power supply voltage, increases with the increase of the electric capacity and tends to be saturated; the surface roughness value of the power supply voltage It increases and increases, and increases with the increase of capacitance.
Aluminum Screw Machined Parts,Custom Cnc Aluminum Screw Machined Parts,Aluminum Machined Parts,Machined Aluminium Parts
Stand Dragon Industrial Co., Ltd. , https://www.standdragontw.com