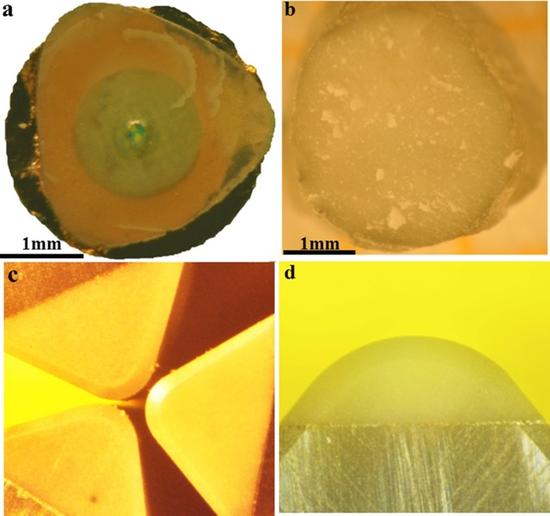
Abstract Diamond-cBN alloy samples and cutters: a and b: Alloy samples with a diameter of 3 mm synthesized at 20 GPa/2200 °C show transparency on copper screens. c and d: diamond-cBN alloy cutting knife polished flank. (The picture comes...
The researchers developed a superhard material by fusing diamonds and cubic boron nitride using a new alloying method.
Washington, September 8, 2015 - People say that diamonds are solid, which is of course oxidized except when they are used to cut iron, cobalt, nickel, chromium, and vanadium at high temperatures. In contrast, cubic boron nitride has excellent chemical inertness, but its hardness is only half that of diamonds. In order to develop a superhard material suitable for various materials in the industry, researchers at Sichuan University in China have created an alloy of diamond and cubic boron nitride, which combines the excellent properties of the two materials.
“Diamonds and cubic boron nitride are very easy to form alloys to fill each other's performance defects, because they are similar in lattice structure and covalent health characteristics,†said Sichauan University's Institute. of Atomic and Molecular Physics), Professor He Duanwei said. “But the idea has never been confirmed, because the samples obtained in previous studies are too small to test their actual performance.â€
He and Professor of the University of Nevada (University of Nevada) and the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Chinese Academy of Sciences) of the collaborators of the study, published this week by the American Institute of Physics 'Applied Physics Letters' in.
In order to synthesize the diamond-cBN alloy, the researchers uniformly mixed the diamond and cubic boron nitride powder, placed in a vacuum furnace and calcined at 1300 Kelvin for two hours, then at a pressure of 15 gigapascals or more and above 2000 Kelvin. The material was pressed into pellets having a diameter of 3.5 mm under high temperature conditions. The ball is polished and sharpened to become a cutting tool.
The researchers tested the properties of the alloy's hardened steel and granite strips on a CNC lathe. They found that the diamond-cBN alloy exhibited comparable wear and tool life to polycrystalline cubic boron nitride when cutting hardened steel samples and showed significantly less wear when cutting granite. In addition, this alloy exhibits better high-speed cutting performance than any polycrystalline cubic boron nitride or commercial polycrystalline diamond.
Professor He and his collaborators will next develop technologies for the manufacture of centimeter-size diamond-cBN alloys to pave the way for industrial scale production.
Laser Stage Light,Dmx Laser,Mini Laser Lighting,Led Laser Moving Head
Big Dipper Laser Science And Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.bigdipper-laser.com